
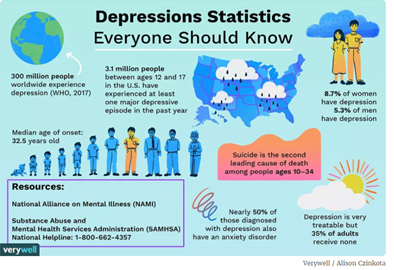
Depression, a very common but serious mental disorder where a person lacks his or her interest and pleasure in daily activities leading to significant weight loss or gain, insomnia or excessive sleeping. It is also associated with lack of energy, inability to concentrate, feelings of worthlessness or excessive guilt and recurrent thoughts of death or suicide. Globally an estimated 300 million people of all ages suffer from depression. According to Anxiety and Depression Association of America (ADAA) 2 out of 100 young children and 8 out of 100 teens may have serious depression. World wide depression is a leading cause of disability and a major contributor to the overall global burden of disease.
Though depression is common in all ages but elderly are at higher risk of depression. Women are more prone to be depressed than man. Any death or loss, abuse (physical, sexual or emotional), conflicts within person, family members or friends are common causes of depression. Family history of depression may increase the risk, and any major events good or bad acts as a triggering factors of depression.
Child development especially stressful home life in early childhood, parental disharmony, familial conflict, discrepancy in school and adverse environmental issues increases the risk of depression. Other physical illnesses, like diabetes, cancer, heart disease, and chronic pain can causes depression. Depression can make these conditions worse, and vice versa. Certain medications taken for illnesses like isotretinoin (used to treat acne), the antiviral drug interferon-alpha, and corticosteroids, can increase the risk of depression.
Common symptoms of depression are
Children - anxious, cranky, pretend to be sick, refuse to go to school, cling to a parent, or worry that a parent may die.
Older children and teens - easily frustrated‚ restlessness, or have low self-esteem. anxiety, eating disorders, excessive sleepiness (called hypersomnia), increased appetite (called hyperphagia), attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder, or substance use disorder.
Younger adults - irritable, weight gain ,hypersomnia, negative view of life and the future, generalized anxiety disorder, social phobia, panic disorder, and substance use disorders.
Middle-aged adults - decreased libido, middle-of-the-night insomnia, or early morning awakening, gastrointestinal symptoms such as diarrhea or constipation.
Older adults - sadness or grief, lack of emotions. In severe cases, memory and thinking problems (called pseudodementia) may be prominent.
Depression can be treated by –
1. Exercise regularly
2. Reduce social media time
3. Build strong relationships with family and friends
4. Minimize daily choices to reduce conflict
5. Reduce stress by -
6. Maintain treatment plan
7. Get adequate sleep
8. Stay away from toxic people
9. Eat well balanced diet
10. Maintain a healthy weight
11. Manage chronic conditions
12. Avoid over the counter drug. Read prescription medication side effects carefully
13. Reduce alcohol and drug use
14. Get rid of nicotine
15. Plan for unavoidable known triggers

1. Depression - WHO | World Health Organization. Available from: https://www.who.int › Newsroom › Fact sheets › Detail
2. Depression - American Psychological Association. Available from: https://www.apa.org › topics › depression
3. NIMH » Depression - National Institute of Mental Health. Available from: https://www.nimh.nih.gov › health › topics › depression
4. Bruce DF. Causes of Depression: Genetics, Illness, Abuse, and More. Available from: https://www.webmd.com › Depression › Guide
5. Gotter A. How to Avoid Depression: Prevent Relapse and Avoid Triggers. Available from: https://www.healthline.com › health › how-to-avoid-de...